- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Tuberculosis and its medicatioinls increase risk of gout in patients: Study
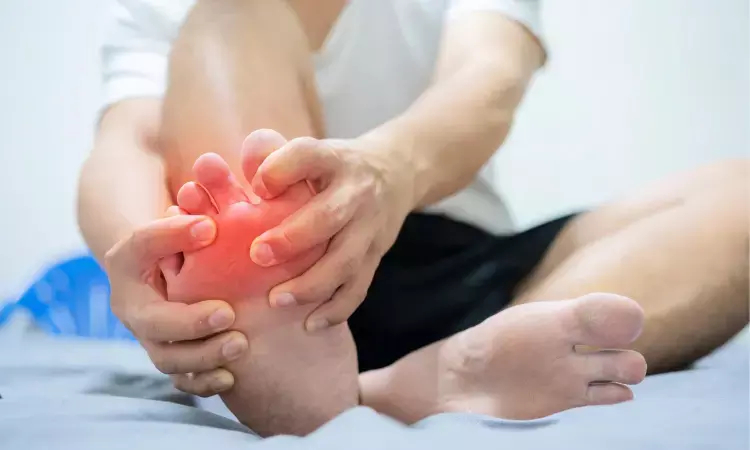
A new study published in the recent issue of International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases showed that the need for greater clinical awareness in this population is highlighted by the higher incidence of gout in tuberculosis (TB) patients and the correlation between comorbidities and TB treatments.
Gout is one of the most prevalent types of inflammatory arthritis in adults. Even while acute gout attacks usually go away on their own in two weeks, if treatment is not received, repeated pain episodes may worsen and lead to the chronic stage of the condition. Globally, tuberculosis is a very common illness and a serious public health issue. It is believed that medications used to treat tuberculosis (TB) raise uric acid levels and affect the development of gout. And so, assessing the risk of gout in TB patients was the aim of this investigation.
This research looked for incident cases of tuberculosis in the South Korean National Health Claims database for this investigation. Standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) were used to quantify the risk in comparison to the general population after gout patients who had been diagnosed within 6 months of a TB diagnosis were identified. Thus, to determine the risk variables for gout, this study among TB patients was conducted by comparing people with and without gout in a 1:5 ratio.
Males, patients aged ≥70 years, and those diagnosed within the first 2 months made up 70.2%, 33.0%, and 52.8% of the 3848 gout patients, respectively. When compared to the general population, TB patients had a noticeably greater prevalence of gout. Gout was linked to heart failure, pyrazinamide and ethambutol usage, chronic renal disease, and hypertension, according to conditional logistic regression analysis.
Overall, this study found that TB patients are more likely than the general population to get gout. Gout in TB patients was linked to underlying conditions such heart failure, hypertension, chronic renal disease, and the use of pyrazinamide (PZA) and ethambutol (ETB), highlighting the need for increased gout awareness in this patient population.
Source:
Kim, C. Y., Ha, J. W., Jung, I., Han, M., & Ahn, S. S. (2025). Risk of gout among patients with tuberculosis: A nationwide cohort study in South Korea. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, 28(3), e70197. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.70197
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


